ResNet을 제시한 논문 "Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition"을 params# 측면에서의 주요 컨셉을 코드 및 시각화로 리뷰합니다.
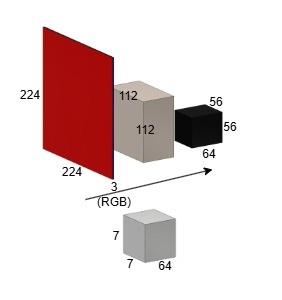
$$\text{conv_params}=\text{input_ch}×\text{output_ch}×\text{kernel_w}×\text{kernel_h}+\text{bias}$$
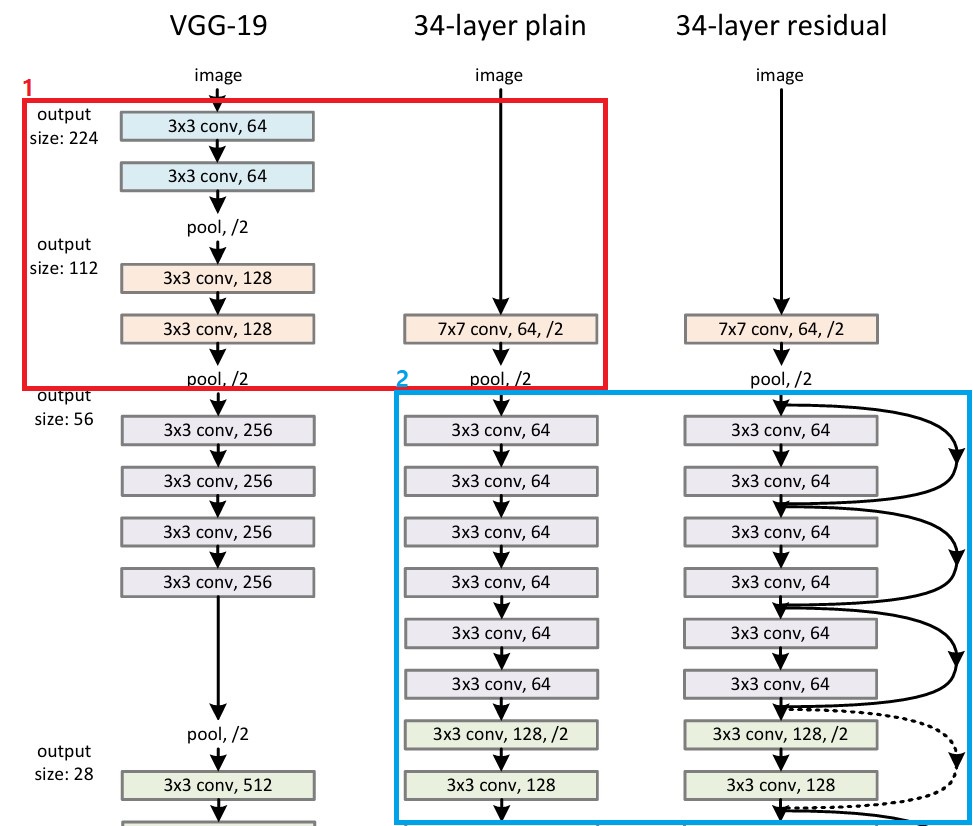
1. 첫 레이어
| 비교 | VGG's | ResNet's |
| params# | 260,160 | 9,472 |
# VGG
import torch.nn as nn
module = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding='same'),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding='same'),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding='same'),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding='same'),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
>
----------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Conv2d-1 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 1,792
Conv2d-2 [-1, 64, 224, 224] 36,928
MaxPool2d-3 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 0
Conv2d-4 [-1, 128, 112, 112] 73,856
Conv2d-5 [-1, 128, 112, 112] 147,584
MaxPool2d-6 [-1, 128, 56, 56] 0
================================================================
Total params: 260,160# ResNet
import torch.nn as nn
module = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
)
>
----------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Conv2d-1 [-1, 64, 112, 112] 9,472
MaxPool2d-2 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 0
================================================================
Total params: 9,472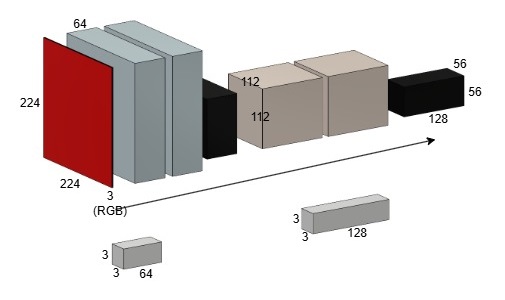
$$ \begin{aligned} & \textbf{VGG's parameters:} \\[0.5em] 260,160 = &\; (3 \times 64 \times 3 \times 3 + 64) \\ &+ (64 \times 64 \times 3 \times 3 + 64) \\ &+ (64 \times 128 \times 3 \times 3 + 128) \\ &+ (128 \times 128 \times 3 \times 3 + 128) \end{aligned} $$ $$ \begin{aligned} & \textbf{ResNet's parameters:} \\[0.5em] 9,472 = &\; (3 \times 64 \times 7 \times 7 + 64) \end{aligned} $$
ResNet은 VGG에 비해 성능 지표(accuracy 등)가 더 우수할 뿐 아니라, Bottleneck 구조 덕분에 파라미터 수와 연산량이 줄어들어 더 효율적인 계산이 가능하며, 결과적으로 더 빠른 속도를 보일 수 있습니다.
2. Bottleneck 레이어
사실 Figure 3에서 표시한 34-layers에는 `x + y`를 설명할 뿐, Bottleneck을 설명할 수 없지만 params# 측면에서는 bottleneck이 더 두드러져 적용하여 설명하였습니다.
| 비교 | plain (ConvBlock) (숏컷 없음) | BottleneckBlock (실선) | BottleneckBlock (점선) |
| params# | 73,856 | 45,248 | 57,728 |
| Residual | X | O | O |
| Bottleneck | X | O (논문은 X) | O (논문은 X) |
| 차원 변환 | 64 -> 64 | 64 -> 64 | 64 -> 128 |
import torch.nn as nn
class ConvBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding):
super(ConvBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
return x
module = ConvBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding='same')
>
----------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Conv2d-1 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 36,928
Conv2d-2 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 36,928
================================================================
Total params: 73,856import torch.nn as nn
class BottleneckBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding):
super(BottleneckBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
return x + y
module = BottleneckBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding='same')
>
----------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Conv2d-1 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 4,160
Conv2d-2 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 36,928
Conv2d-3 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 4,160
================================================================
Total params: 45,248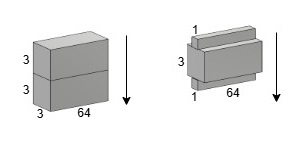
$$ \begin{aligned} \textbf{plain's parameters:} \\[0.5em] 73,856 = &\; (64 \times 64 \times 3 \times 3 + 64) \\ &+ (64 \times 64 \times 3 \times 3 + 64) \end{aligned} $$ $$ \begin{aligned} \textbf{bottleneck's parameters:} \\[0.5em] 45,248 = &\; (64 \times 64 \times 1 \times 1 + 64) \\ &+ (64 \times 64 \times 3 \times 3 + 64) \\ &+ (64 \times 64 \times 1 \times 1 + 64) \end{aligned} $$
점선으로 표시된 숏컷은 차원 수가 바뀌는 경우를 뜻합니다. (input 64 -> output 128)
input과 output의 dimension이 달라져, 차원 수를 맞춰줄 `conv_shortcut`으로 input `x`를 전처리합니다.
import torch.nn as nn
class BottleneckBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding):
super(BottleneckBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channels, out_channels=out_channels*2, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv_shortcut = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels*2, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
y = self.conv1(x)
y = self.conv2(y)
y = self.conv3(y)
x = self.conv_shortcut(x)
return x + y
module = BottleneckBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
>
----------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
================================================================
Conv2d-1 [-1, 64, 56, 56] 4,160
Conv2d-2 [-1, 64, 28, 28] 36,928
Conv2d-3 [-1, 128, 28, 28] 8,320
Conv2d-4 [-1, 128, 28, 28] 8,320
================================================================
Total params: 57,728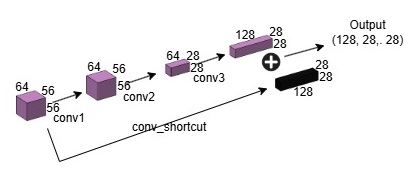
$$ \begin{aligned} \textbf{bottleneck's parameters:} \\[0.5em] 57,728 = &\; (64 \times 64 \times 1 \times 1 + 64) \\ &+ (64 \times 64 \times 3 \times 3 + 64) \\ &+ (64 \times 128 \times 1 \times 1 + 128) \\ &+ (64 \times 128 \times 1 \times 1 + 128) \end{aligned} $$
'개발' 카테고리의 다른 글
| JetPack6로 업그레이드하기. (NVIDIA Jetson Nano Orin Developer Kit) (0) | 2025.03.29 |
|---|---|
| YOLOv5 C3 Block 시각화 리뷰 (0) | 2025.03.28 |
| 딥시크(DeepSeek-R1-Zero) 논문 리뷰 (0) | 2025.01.31 |
| 라즈베리파이4와 스텝 모터 드라이버 연결 및 문제 해결 과정 (1) | 2025.01.03 |
| Next.js Introduction (0) | 2024.04.20 |